Are fish affected by Mycotoxins?
Mycotoxins are recognized as a global issue in agricultural production, both in livestock and aquaculture segment.
There is an increasing trend to use more and more plant ingredients in aquaculture feed caused by high prices of fishmeal and oils.
With this trend, the risk of mycotoxin contamination also increases, affecting fish growth performance as well as final product quality.

What types of mycotoxins mainly affect fish animals?
Five most common Mycotoxins found worldwide in aquafeed and raw material used for feed formulation:
- Aflatoxins (Afla),
- Zearalenone (ZEN),
- Trichotecenes (T-2 & HT-2),
- Fumonisins (FUM),
- Ochratoxin A (OTA).


Which species are more affected?
Level of damage that can be caused by the Mycotoxins intake depends mainly on the type of toxin, its concentration in the feed and time period of exposure, as well as animal species susceptibility.
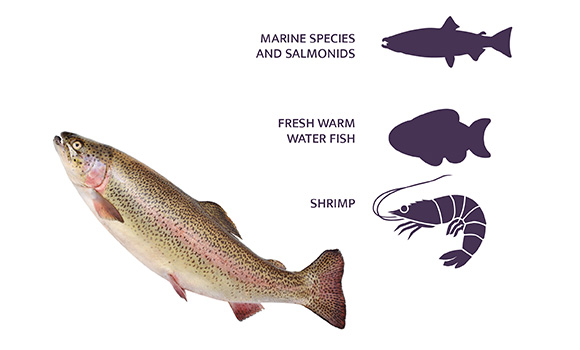
Considering this, mycotoxin risk levels for aquatic species have been considered in terms of three categories:
- Marine species and salmonids: Trout, sea bream and sea bass
- Fresh warm-water fish: Tilapia, carp, channel catfish, African catfish, pangasius
- Shrimp: Based on studies with whitelef shrimp and tiger shrimp.
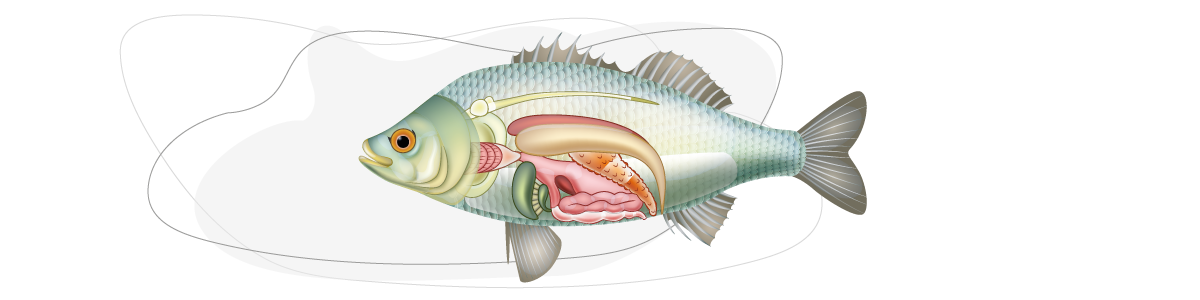
Which organ will be affected depends exclusively on the type and amount of mycotoxin.
Aflatoxin
According to this, the target organ for Aflatoxin is liver, causing liver necrosis and liver carcinom.
Beside, Aflatoxin can produce different damages and pathological manifestations such as:
- Small cell carcinoma
- Palle gills
- Abnormalities in shrimp hepatopancreas.
Ochratoxin A
Ochratoxin A:
- Induce mutagenic and toxic effects
- Degeneration of kidneys and liver
- Provoque poor performances.
Zearalenone
Zearalenone is a mycotoxin which dominantly affects:
- Reproductive parameters in different aquatic species
- Causing change of relative fecundicity,
- Acceleration of sexual maturation
- Reducing of spawning frequency
Fumonisins
FUM has been generally associated with:
- Reduced growth rate
- Lower feed consumption
- Poorfeed efficiency ratio
- impaired sphingolipid metabolism
- Cause lesions in exocrine and endocrine pancreas as well in inter-renal tissue
Trichothecenes
Trichotethenes presence is related to decreased production of bacterial cell wall breaking enzymes and decreased resistance to oxidative damage.
In shrimp T-2 and HT-2 leads to in homogenous growth and physiological disorders.
However, what is the most important is that ALL MYCOTOXINS are immunosuppresive, ALL MYCOTOXINS are increasing mortality and cause poor productive performances. (growth, FCR, daily intake)

Which raw materials and other vectors are the main causes?
The most common plant feedstuffs used in aquafeeds are:
- Corn
- Soybean meal
- DDGS
- Canola
- Cottonseed
- Peas/lupins
- Rice bran
- Cassava
- Wheat


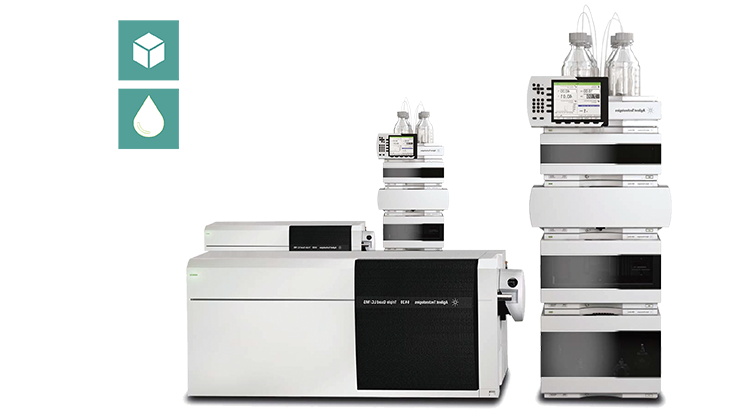
What detection methods are used to detect Mycotoxins in fish?
Mycotoxins in feed are commonly detected and quantified using antibody-based assays and chromatography techniques.
ELISA test
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based assay that is commonly used for Mycotoxins detection.
There are several commercial ELISA kits available for aflatoxins, deoxynivalenol, fumonisins, ochratoxins and zearalenone.
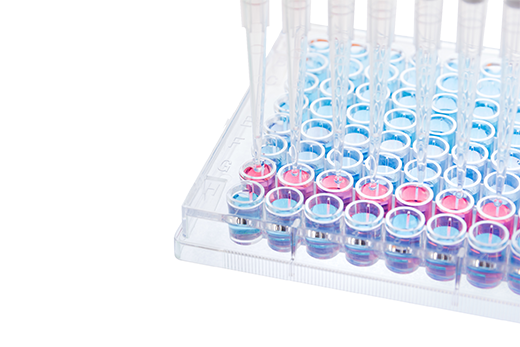
Chromatography and Spectrometry ( HPLC , GG/MS and LC-MS/MS)
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) are two of the most commonly used methods for the detection and quantification of Mycotoxins.
HPLC and GC/MS, apart from having detection limit of < 0.05 ppm for many Mycotoxins, also require expensive equipment and technical support.
LC-MS/MS is a technique that can analyse all Mycotoxins, with increased sensitivity, precision and reproducibility.

How do we prevent from and/or fight against Mycotoxins in fish?
Handling mycotoxin contamination and health consequences in animal production pose increasing challenges for food security and safety systems of the consumer.
In addition to controlling temperature and humidity using aeration, it is advisable to use fungal inhibitors and to use protection against damage caused by insects and rodents.
Despite all the efforts made in order to reduce the level of Mycotoxins in feed ingredients, there is always a certain degree of contamination that may pose a risk to livestock animals.
Mycotoxins are always present, at least in small amounts, and the effects of the presence of those small amounts of diverse Mycotoxins results in synergitics effects that can be greater than the sum of the individual effects that we have described for each type of mycotoxin.
Prevention against Mycotoxins, is necessary and the use of detoxifying or adsorbing agents in fish rations is essential.




 Micotoxicosis prevention
Micotoxicosis prevention