Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites of low molecular weight and therefore test methods for analysis of mycotoxins face different problems ranging from the need to have a well-equipped laboratory, in terms of instrumentation and analytical capacity, to personnel with sufficient experience in handling of samples and reference standards.
Mycotoxins in feed are commonly detected and quantified using antibody-based assays and chromatography technique.
Immunochemical Methods in Mycotoxin detection
Mycotoxin are not antigenic. That is why one of the first developed studies were focused on how to achieve conjugation with proteins or polypeptides that could serve as transporters of antibody production in rabbits and other animals under the optimal conditions.
Different types of immunoassays were developed, among which the most important ones are:
- ELISA test (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
- RIA (radioimmunoassay)
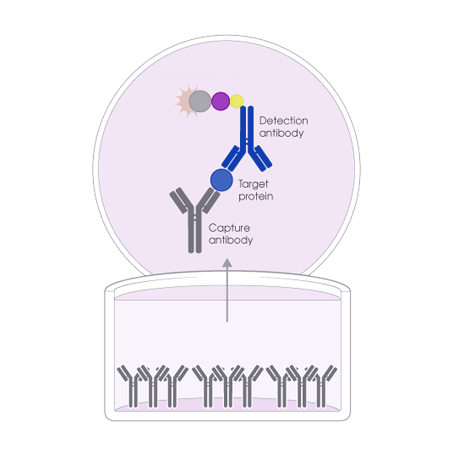
ELISA test
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based assay that is commonly used for mycotoxins detection.
Affordable methods
There are several commercial ELISA kits available for Aflatoxins, Deoxynivalenol, Fumonisins, Ochratoxins and Zearalenone.
ELISA is one of the most affordable methods for mycotoxins detection, but the limit of detection for many mycotoxins often exceeds 0.2 ppm.

Instrumental methods
Chromatography and Spectrometry
The use of chromatographic techniques requires prior preparation of a sample using different methods of extraction and purification. Depending on the mycotoxins to be analysed and the feed matrix, different types of techniques such as immunoaffinity columns based preparations or other procedures based on solid-liquid (Quechers, DMFS, etc.) or liquid-liquid (DLLME) extractions are used.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) are two of the most commonly used methods for the detection and quantification of mycotoxins.
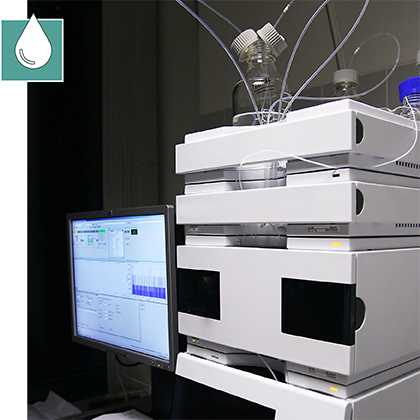

High-performance liquid chromatography

Gas chromatography
Abssorption and emission spectrometric techniques
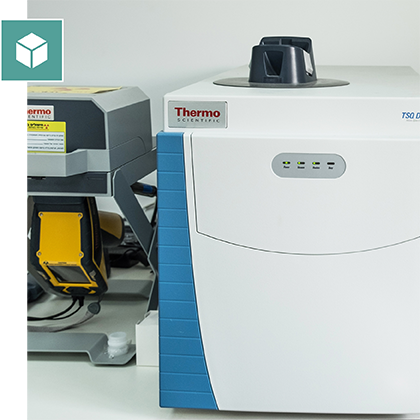

Mass spectrometry
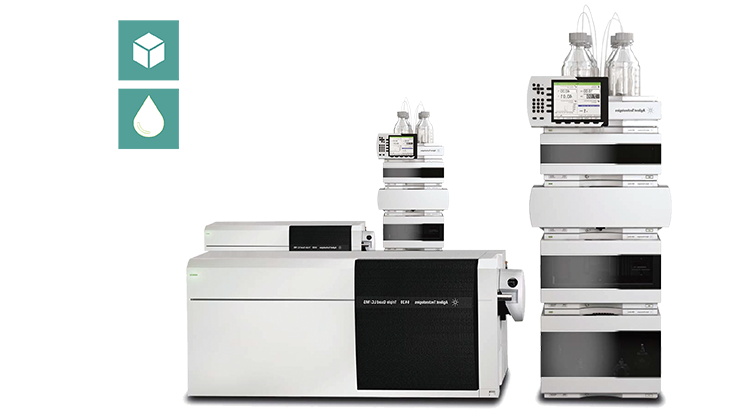
Liquid chromatography coupled to a tandem mass spectrometry detector
Liquid chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS) is nowadays the gold standard for the evaluation of mycotoxins and the most reliable way of their quantification.




 Micotoxicosis prevention
Micotoxicosis prevention