OBJETIVE
OBJETIVE
 Mycotoxins present a significant health concern within the animal feed industry, with profound implications for the pig farming sector.
Mycotoxins present a significant health concern within the animal feed industry, with profound implications for the pig farming sector.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of two commercial adsorbents, an organically modified clinoptilolite (OMC) and a multicomponent mycotoxin detoxifying agent (MMDA), to ameliorate the combined adverse effects of dietary aflatoxins (AFs: sum of AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2), fumonisins (FBs), and zearalenone (ZEN) at levels of nearly 0.5, 1.0, and 1.0 mg/kg, respectively, on a cohort of cross-bred female pigs (N = 24).

MATERIALS & METHODS
MATERIALS & METHODS
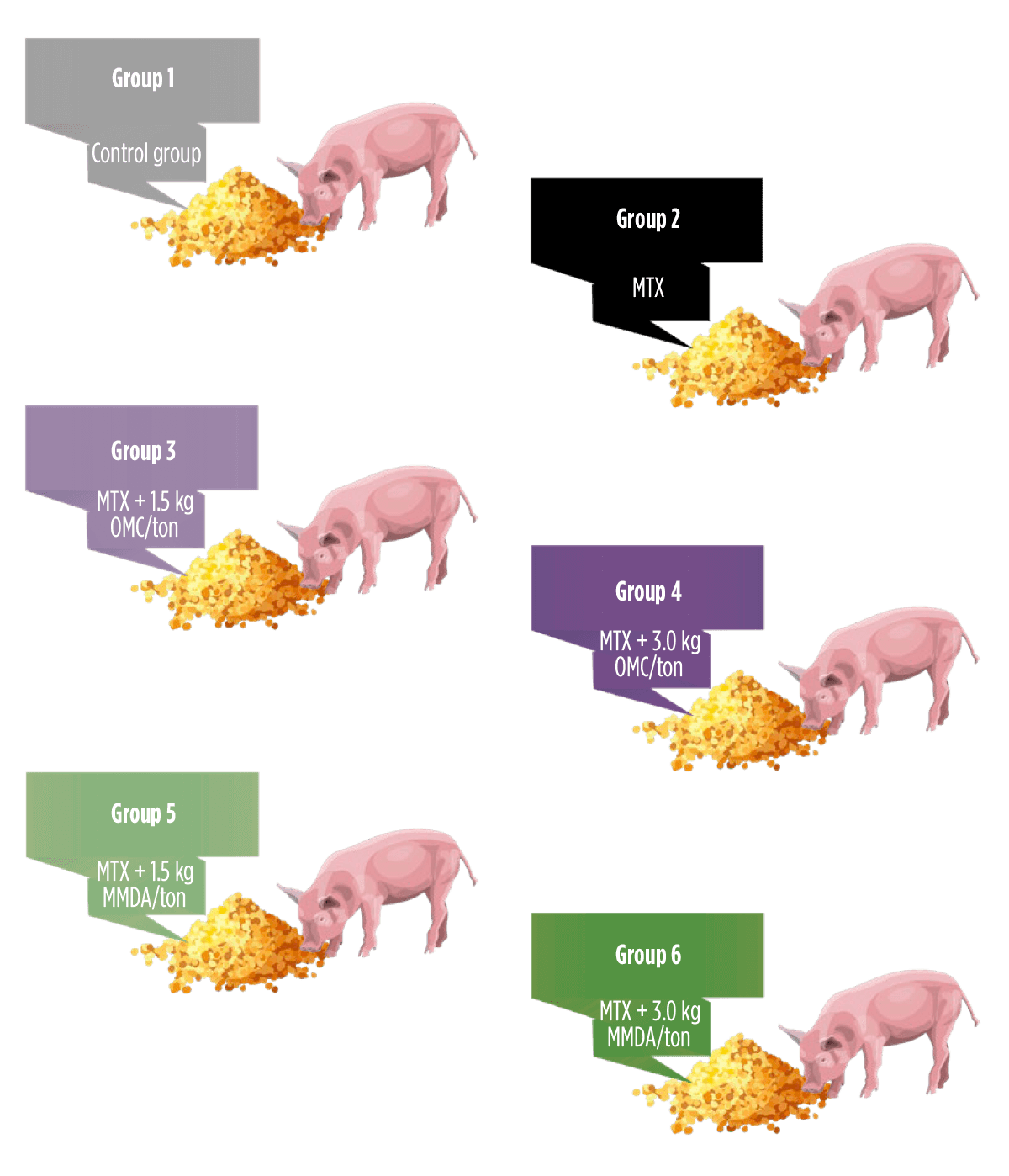
![]() Pigs were randomly allocated into six experimental groups, each consisting of four individuals, and subjected to a dietary regimen spanning 42 days:
Pigs were randomly allocated into six experimental groups, each consisting of four individuals, and subjected to a dietary regimen spanning 42 days:
- ⇰ Group 1: control group
- ⇰ Group 2: mycotoxins (MTX) alone (0.5 mg AFs/kg + 1.0 mg FBs/kg + 1.0 mg ZEN/kg)
- ⇰ Group 3: MTX (0.5 mg AFs/kg + 1.0 mg FBs/kg + 1.0 mg ZEN/kg) + 1.5 kg OMC/ton
- ⇰ Group 4: MTX (0.5 mg AFs/kg + 1.0 mg FBs/kg + 1.0 mg ZEN/kg) + 3.0 kg OMC/ton
- ⇰ Group 5: MTX (0.5 mg AFs/kg + 1.0 mg FBs/kg + 1.0 mg ZEN/kg) + 1.5 kg MMDA/ton
- ⇰ Group 6: MTX (0.5 mg AFs/kg + 1.0 mg FBs/kg + 1.0 mg ZEN/kg) + 3.0 kg MMDA/ton
RESULTS
RESULTS
 The combined administration of AFs, FBs, and ZEN (Group 2) reduced the body-weight gain and increased the relative weight of the liver, while there was no negative influence observed on the serum biochemistry of animals.
The combined administration of AFs, FBs, and ZEN (Group 2) reduced the body-weight gain and increased the relative weight of the liver, while there was no negative influence observed on the serum biochemistry of animals.
In contrast, supplementation of OMC and MMDA (Groups 3, 4, 5, and 6):
 Ameliorated the toxic effects of these mycotoxins, which was demonstrated by the histological findings in the liver and kidneys.
Ameliorated the toxic effects of these mycotoxins, which was demonstrated by the histological findings in the liver and kidneys. Resulted in a notable reduction in residual levels of AFs, FBs, and ZEN in the liver and kidneys.
Resulted in a notable reduction in residual levels of AFs, FBs, and ZEN in the liver and kidneys.
 Moreover, supplementation of OMC was able to inhibit the initiation of liver carcinogenesis without any hepatotoxic side effects.
Moreover, supplementation of OMC was able to inhibit the initiation of liver carcinogenesis without any hepatotoxic side effects.
|
These findings demonstrate that the use of OMC and MMDA effectively mitigated the adverse effects of dietary AFs, FBs, and ZEN in piglets.
|
Authors
Micheli Midori de Cerqueira Costa Aoyanagi1, Fábio Enrique Lemos Budiño2, Jog Raj3, Marko Vasiljević3, Sher Ali1, Leandra Naira Zambelli Ramalho4, Fernando Silva Ramalho4, Carlos Humberto Corassin1, Giovana Fumes Ghantous5 , and Carlos Augusto Fernandes de Oliveira1
1Department of Food Engineering, Faculty of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA), University of São Paulo (USP), Brazil
2Department of Agriculture and Food Supply of the São Paulo State, Institute of Animal Science and Pastures, Brazil
3Patent Co., DOO., Serbia
4Department of Pathology and Legal Medicine, School of Medicine at Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo (USP), Brazil
5Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA), University of São Paulo (USP), Brazil
Aoyanagi, M.M.d.C.C.; Budiño, F.E.L.; Raj, J.; Vasiljevi´c, M.; Ali, S.; Ramalho, L.N.Z.; Ramalho, F.S.; Corassin, C.H.; Ghantous, G.F.; Oliveira, C.A.F.d. Efficacy of Two Commercially Available Adsorbents to Reduce the Combined Toxic Effects of Dietary Aflatoxins, Fumonisins, and Zearalenone and Their Residues in the Tissues ofWeaned Pigs. Toxins 2023, 15, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15110629




 Further studies should explore the long-term protective effects of the studied adsorbent supplementation to optimize mycotoxin management strategies in pig-farming operations.
Further studies should explore the long-term protective effects of the studied adsorbent supplementation to optimize mycotoxin management strategies in pig-farming operations. Micotoxicosis prevention
Micotoxicosis prevention