Description
Soy or Soybean (Glycine max) is a species of the family Fabaceae, or family of legumes. It is cultivated for its seeds, medium oil content (being an oleaginous plant) and high protein content. Soybeans and their by-products (Soybean oil and flour) are used in human food, livestock and poultry. It is marketed all over the world due to its multiple uses.
Soy is a food very rich in protein.
- It is composed of 40% protein and 20% oil.
- The rest of its content is composed of 35% carbohydrates and about 5% ash.

Cultivated
The optimum temperatures for Soybean growth are between 20 and 30ºC, while the temperatures near 30ºC are the most ideal for their growth.
- Vegetative growth of Soybeans is small or almost non-existent when temperatures are close to or below 10ºC. Their growth stops at temperatures below 4ºC, although Soybeans plants can withstand temperatures between -2 to -4ºC without dying.
- Temperatures higher than 40º C cause an undesired effect on the growth rate, causing damage to flowering.

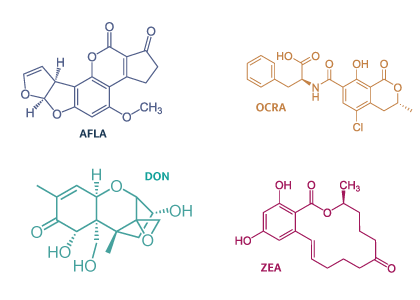
Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins found mainly in Soybean/s:
- Aflatoxins
- Ochratoxins
- Type B Trichothecene
- Zearalenone
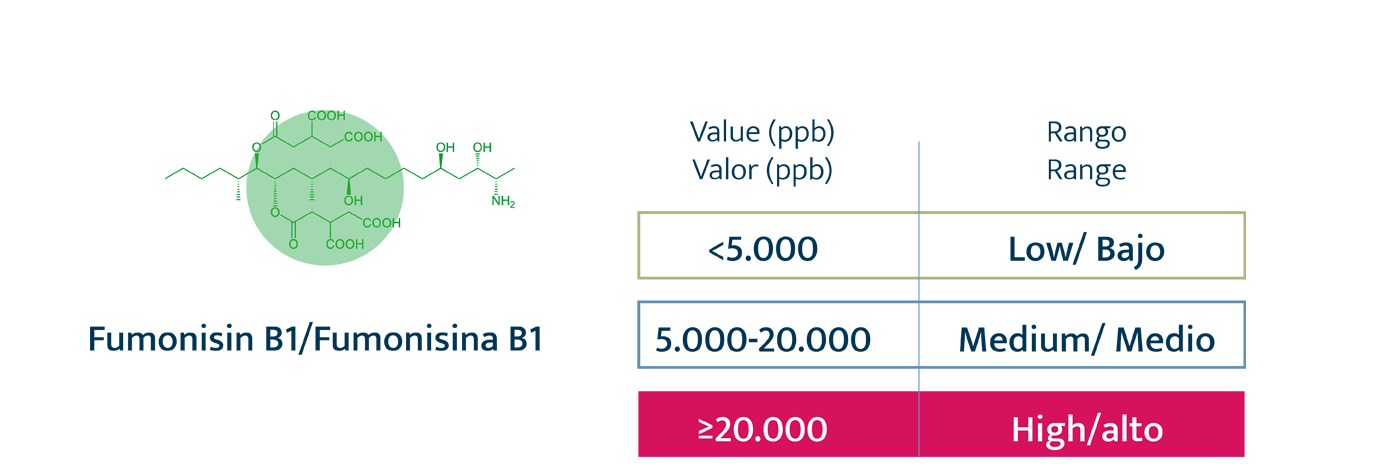
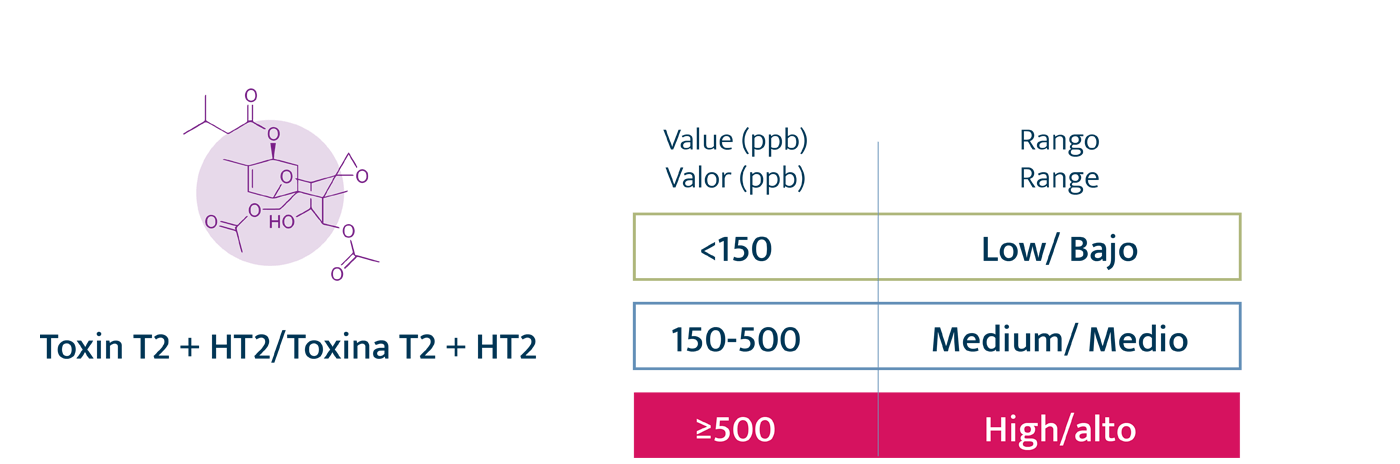
Levels
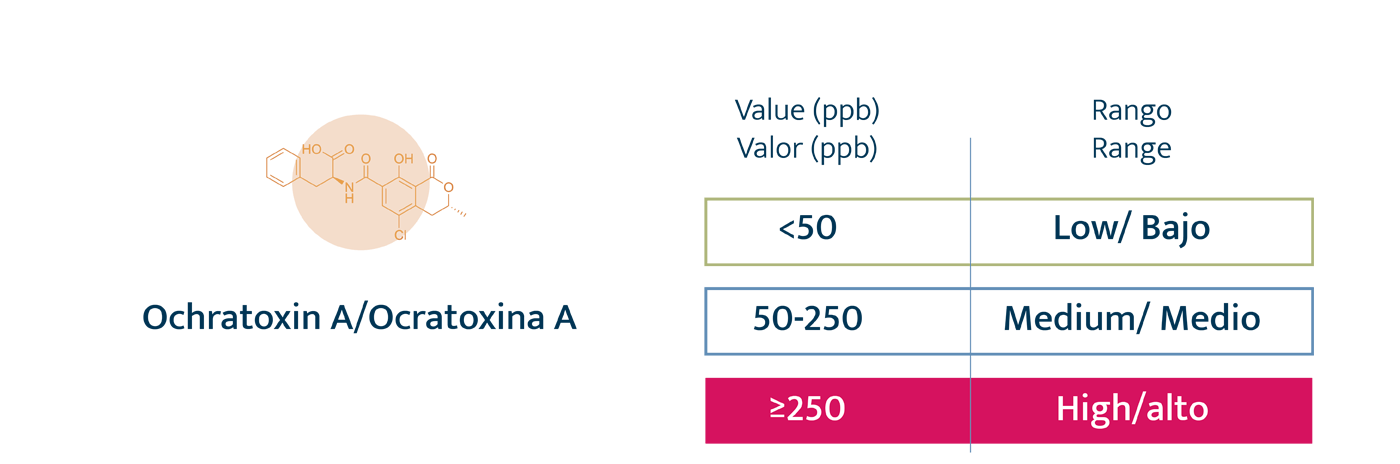
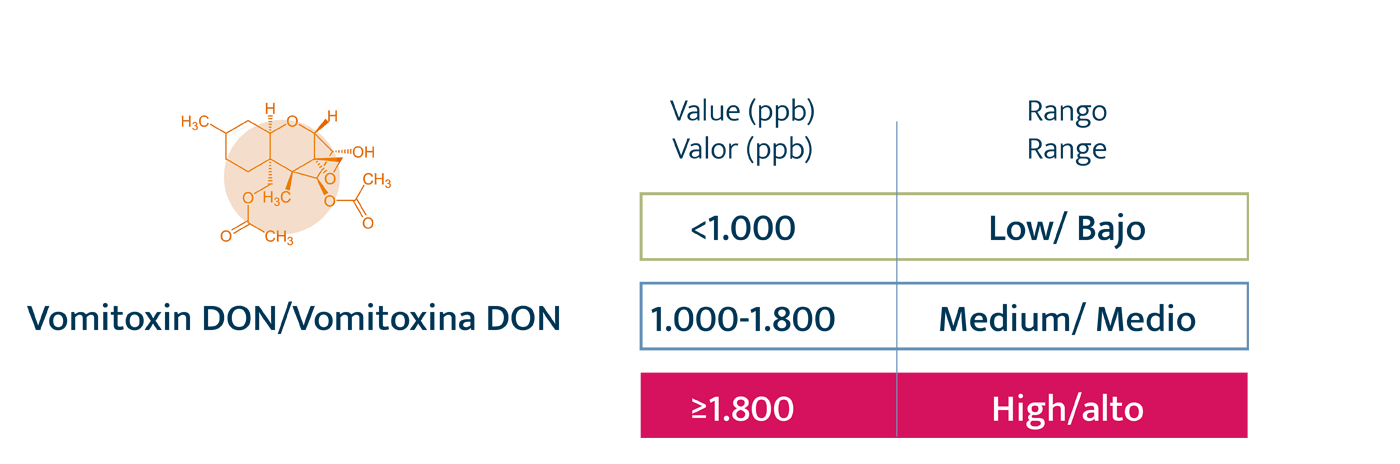
Authorized and recommended levels of mycotoxins
Legal restrictions. Exclusively for AFB1, with a maximum of 20 ppb in any raw material for animal feed.











 Micotoxicosis prevention
Micotoxicosis prevention